
What is a marketplace? Find out how to get the most out of it
What is a marketplace? Find out how to get the most out of it In today’s digital world, marketplaces have
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is an integrated software system that enables companies to manage their business operations in an efficient and centralized manner. These systems connect different departments and functions within an organization, such as accounting, supply chain, production and human resources, with the aim of improving fluidity and consistency in the management of resources and processes. Their use has evolved from being a tool used mainly by large corporations to being an accessible solution for small and medium-sized companies as well, due to technological advances and the migration of these systems to the cloud.
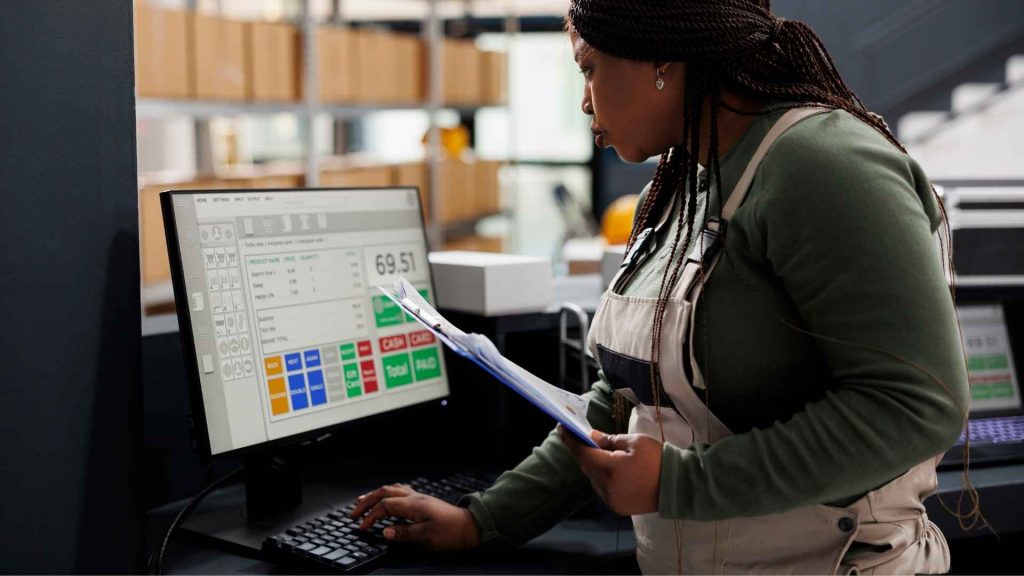

An ERP is essentially a set of modular applications that work together to automate and centralize data and business processes in an organization. ERP systems are capable of integrating various functional areas, from finance to inventory management to sales, purchasing and human resources.
The primary function of an ERP is to eliminate data silos within the enterprise, providing a single source of accurate and up-to-date information for all departments.
This centralized approach allows companies to operate more efficiently and make faster, more informed decisions.
In addition, by automating repetitive tasks, such as invoicing or inventory management, the operational burden is reduced and human error is minimized.
An ERP serves to improve a company’ s operational efficiency, transparency and responsiveness to market demands.
Among its most important uses are:

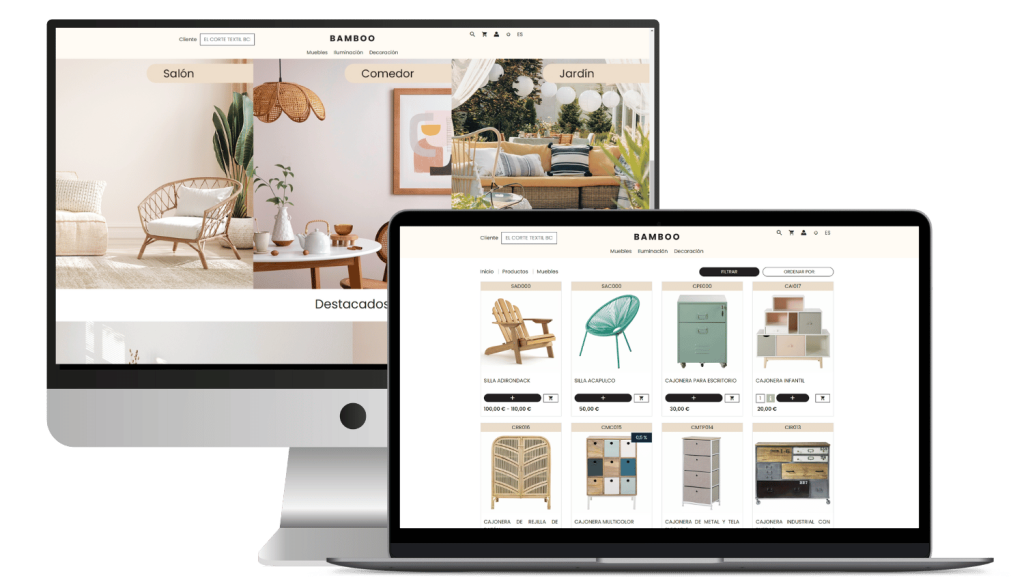
Transform your ERP into a powerful B2B ecommerce system
ERP works through modules that manage each functional area of the company, all interconnected through a single central database. This modular architecture allows companies to choose which functions to integrate according to their particular needs.
Main Features and Functionalities:
Implementing an ERP offers numerous advantages for companies, but it also requires careful planning.
Key Benefits of Using an ERP in Enterprises:
Considerations:

There are two main types of ERP: on-premise and cloud-based systems.
Examples of ERPs in the market:
Determining whether an ERP is right for your business depends on the size, complexity of your operations and the specific challenges you face.
Examples of ERP Implementation in Different Industries:
Before implementing an ERP, evaluate the following factors:
ERP implementation can present significant challenges:
Integrate your ERP with B2B ecommerce with Stoam SaaS


The future of ERP systems is marked by several trends:
These trends indicate that ERP software will continue to evolve, adapting to changing market and business needs.
Share:

What is a marketplace? Find out how to get the most out of it In today’s digital world, marketplaces have

Business to consumer (B2C): how it works and how it differs from B2B In today’s world, e-commerce and direct business-to-consumer

Alibaba revolutionises B2B commerce with ‘Accio’ – the AI-powered search engine for SMEs Share: Tabla de contenidos What is Accio

Examples of market segmentation: How to apply it in different sectors? In today’s competitive business landscape, market segmentation is more

Omni-channel strategy: How to integrate all channels to improve customer experience In a world where consumers use multiple channels to

What are open APIs and their role in SaaS solutions? Open APIs have transformed the way businesses use software, especially

Analysis of B2B marketplaces: Are they an opportunity or a threat? B2B marketplaces are transforming the way companies buy and

How to use chatbots in B2B ecommerce to improve conversions In the world of ecommerce B2B (Business to Business)shopper expectations

ERP and sustainability: How a system can reduce environmental impact Sustainability has become a crucial priority in today’s business landscape.
Automate orders with Stoam SaaS b2b ecommerce
